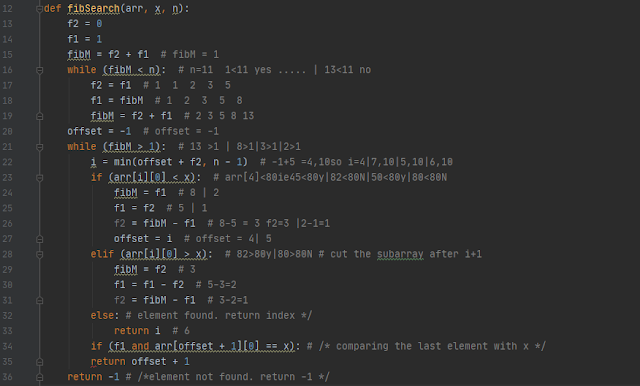
Very good explanation of Fibbonacci Search
Author: Nitin Mohan Shivale
Friday, 31 July 2020
Group B 12[b] Write a python program to store names and mobile numbers of your friends in sorted order on names. Search your friend from list using Fibonacci search. Insert friend if not present in phonebook.
Group B: 12 [a] a) Write a python program to store names and mobile numbers of your friends in sorted order on names. Search your friend from list using binary search (recursive and non-recursive). Insert friend if not present in phonebook
Problem Statement:
a) Write a python program to store names and mobile numbers of your friends in sorted order on names. Search your friend from list using binary search (non recursive and recursive). Insert friend if not present in phone book.
Source Code:
Recursive Function of Binary Search:
The main function calling from here.....
Monday, 20 July 2020
Write a python program to store roll numbers of student in array who attended training program in random order. Write function for searching whether particular student attended training program or not, using Linear search and Sentinel search.
Problem Statement:
a) Write a python program to store roll numbers of student in array who attended training program in random order. Write function for searching whether particular student attended training program or not, using Linear search and Sentinel search.
Theory:
Linear Search :
The idea behind linear search is to compare the search item with the elements in the list one by one (using a loop) and stop as soon as we get the first copy of the search element in the list. Now considering the worst case in which the search element does not exist in the list of size N then the Simple Linear Search will take a total of 2N+1 comparisons (N comparisons against every element in the search list and N+1 comparisons to test against the end of the loop condition).
Sentinel Linear Search :
Here the idea is to reduce the number of comparisons
required to find an element in a list. Here we replace the last element of the
list with the search element itself and run a while loop to see if there
exists any copy of the search element in the list and quit the loop as soon as
we find the search element. See the code snippet for clarification.
Algorithm:
int last = array[N-1];
array[N-1]
= item; // Here item is the search element.
int
i = 0;
while(array[i]!=item)
{
i++;
}
array[N-1]
= last;
if(
(i < N-1) || (item == array[N-1]) )
{
cout << " Item Found @
"<<i;
}
else
{
cout << " Item Not
Found";
}
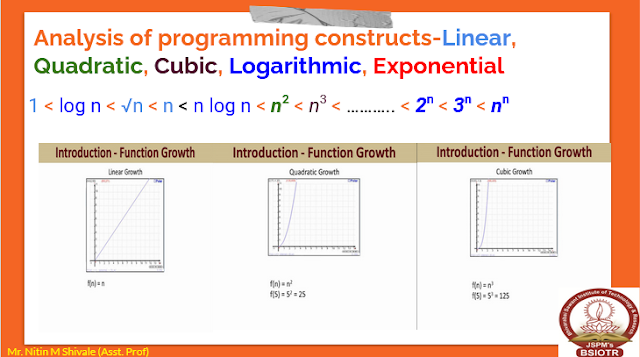
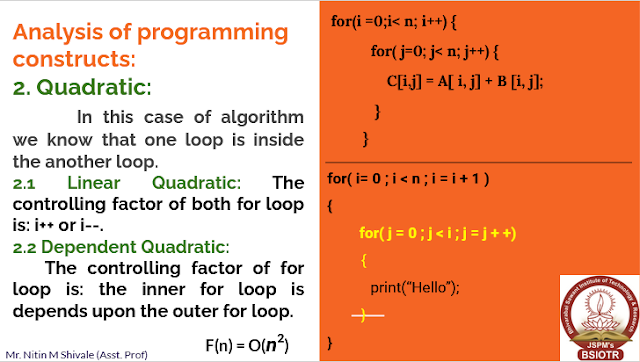
Analysis:
Here we see that the while loop
makes only one comparison in each iteration and it is sure that it will
terminate since the last element of the list is the search element itself. So
in the worst case ( if the search element does not exists in the list ) then
there will be at most N+2 comparisons ( N comparisons in the
while loop and 2 comparisons in the if condition). Which is better than
( 2N+1 ) comparisons as found in Simple Linear Search.
Take note that both the algorithms
have time complexity of O(n).
Program :
Output:
Sentinel Search......
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 44, 55, 30]
8
30
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 44, 55, 30]
key found at location: 7
Write a python program to store roll numbers of student array who attended training program in sorted order. Write function for searching whether particular student attended training program or not, using Binary search and Fibonacci search
Problem Statement:
b) Write a python program to store roll numbers of student array who attended training program in sorted order. Write function for searching whether particular student attended training program or not, using Binary search and Fibonacci search
Reference: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/fibonacci-search/
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)