Unit no 1 Problem Solving, Programming and Python Programming
A problem is a situation that is unsatisfactory and causes difficulties for people and needs to be dealt with or solved.
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
1. Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
2. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
3. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
4. Evaluate options: Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
5. Select the best solution: Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
6. Implement the solution: Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
7. Review and learn: Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
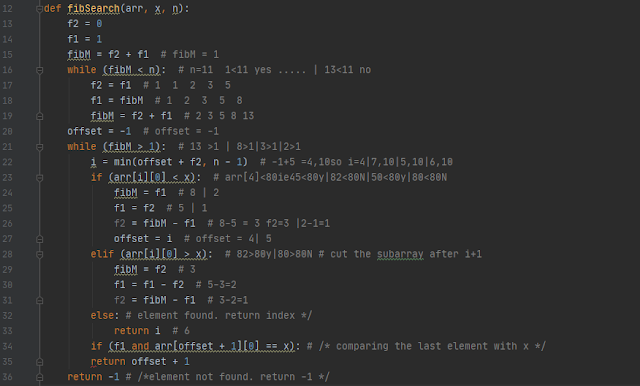
Program Design Tools: Algorithm, Flowchart, Pseudo-codes.
Basics of Python Programming:
2. History of Python: Click here to learn more
3. Literal Constants: click here to learn more.