Wednesday, 3 September 2025
Tuesday, 15 July 2025
In an e-commerce system, customer account IDs are stored in a list write a program to search customer id using linear and binary search.
Savitribai Phule Pune University
Second Year of Computer Engineering and Computer Science and Engineering (2024 Course)
PCC-201A COM: Data Structures Laboratory
Problem Statement:
In an e-commerce system, customer account IDs are stored in a list, and you are tasked with
writing a program that implements the following:
a) Linear Search: Check if a particular customer account ID exists in the list.
b) Binary Search: Implement Binary search to find if a customer account ID exists,
improving the search efficiency over the basic linear
Algorithm:
1. Linear Search:
1. Start
2. Accept Customer ID from user that you want to search in e-commerce system i:e target_id
3. You have to check one by one linearly that target_id is present inside the Customer_Id list.
3.1 if it is present then print or show target _id is present at nth index. or
3.2 if all customer_id scanned or checked and still if you are not getting match of target_id then just print or show customer_id is not present.
4. Stop
2. Binary Search:
1. Start
2. For Binary Search all elements inside the list must be in sorted order. hence sort the list (if not already sorted).
3. Set low = 0 (start index of
the list).
4. Set high = length of the list - 1
(end index).
5. While low is less than or equal
to high,
do:
5.1 Calculate mid
= (low + high) // 2.
5.2 If the element
at mid is equal to the target:
5.2.1 Return
mid
(target found).
5.3 Else if element
at mid is less than the target:
5.3.1 Set
low = mid + 1
(search in right half).
5.4 Else:
5.4.1 Set
high = mid - 1
(search in left half).
6. If the loop ends and the target is
not found:
6.1 Return -1.
Implementation:
Monday, 7 July 2025
Implement student database using dynamically allocated memory and perform various operations.
NEP 2020 Compliant Curriculum Structure
Second Year Engineering (2024 Pattern) – Information Technology
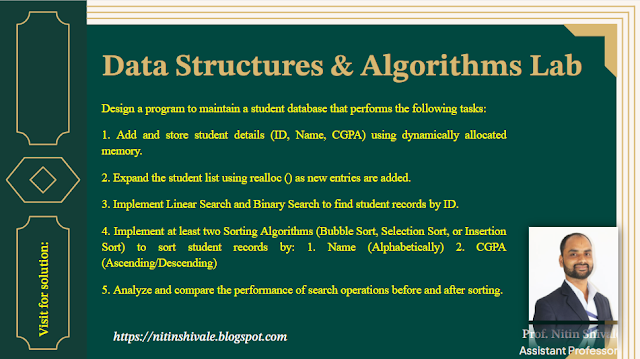
Design a program to maintain a student database that performs the following tasks:
1. Add and store
student details (ID, Name, CGPA) using dynamically allocated memory.
2. Expand the student
list using realloc () as new entries are added.
3. Implement Linear
Search and Binary Search to find student records by ID.
4. Implement at least
two Sorting Algorithms (Bubble Sort, Selection Sort, or Insertion Sort) to sort
student records by: 1. Name (Alphabetically) 2. CGPA (Ascending/Descending)
5. Analyze and compare
the performance of search operations before and after sorting.
5. Algorithms:
Tuesday, 24 June 2025
Implement a robust Java calculator program that computes user input dynamically. ( OOPCGL 2024 Course)
PCC-205-COM: Object Oriented programming and Computer Graphics Lab (2024 Course)
Group A
1. Title: Implement a robust Java calculator program
2. Objective: To explore & understand the principles of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP).
3. Problem Statement: Implement a robust Java calculator program that captures user input dynamically, processes mathematical operations using conditional logic and looping constructs, and ensures efficient error handling.
4. Outcomes:
After implementing the above problem statement, the expected output is as follows:
1. Dynamically user can accept any input.
2. User can perform following mathematical operations using conditional logic (operational rules R) and looping constructs.
2.1 Addition of input a, b (a + b)
2.2 Subtraction of input a, b (a - b)
2.3 Multiplication of input a, b (a * b)
2.4 Division of input a, b (a / b)
2.5 Reminder of input a, b (a % b)
3. Error like divide by zero error gets handle by using try and catch block.
5. Software and Hardware Requirements:
5.1 Software Requirements:
1. Operating System: 64-bit Open-source Linux or its derivative
2. Programming tools: - Open-Source Java Open JDK,
3. Programming IDE: BlueJ, Eclipse, NetBeans, JDeveloper.
5.2 Hardware Requirements:
13th Gen Intel(R) Core (TM) i5-13400 2.50 GHz, 8 GB RAM
6. Mathematical Model:
The model can be expressed as:
Given a, b ∈ R and O ∈ {+
/) and modulus (%)
7. Algorithm:
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Accept input a, b and operator O belongs to +, -, x, / and mod from user dynamically.
Step 3: Now as per the operator following operations are going to be performed.
Step 3.1: if operator is + then show result = a + b
Step 3.2: if operator is - then show result = a - b
Step 3.3: if operator is * then show result = a * b
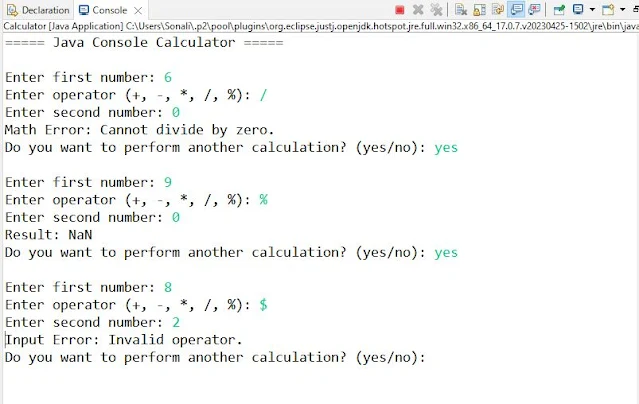
Step 3.4: if operator is / then check the constraint b (b! =0) is not equal to zero if this constraint is true then you have to throw the exception and handle it by using catch block. else if this constraint is false you have to do normal operation & show result = a / b.
Step 3.5: if operator is % (mod) then check the constraint b (b! =0) is not equal to zero if this constraint is true then you have to throw the exception and handle it by using catch block. else if this constraint is false you have to do normal operation & show result = a % b.
Step 4: Stop
8. Flowchart:
9. Program Code:
10. Sample Output:
Test Case: 02 Inputs to test Exception Handling
11. Conclusion:
Hence, we learn how to apply fundamental programming constructs in Java for implementing an application.